Introduction: Start by explaining the importance of choosing the right inverter for your home’s power needs, especially with frequent power outages in certain areas.
Wattage and Load Calculation: Guide readers through calculating their household energy requirements to determine the correct inverter capacity.
Types of Inverters: Provide a breakdown of the different types of inverters like sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave.
Efficiency and Battery Compatibility: Explain how inverter efficiency affects power consumption and discuss compatible battery types, including lead-acid and lithium-ion.
Price vs Quality: Help users understand how to balance budget constraints with quality and performance, including brand comparisons.
Conclusion: Offer a quick checklist for choosing the best inverter for home use.
Understanding Inverter Types: Pure Sine Wave vs Modified Sine Wave
Introduction: Explain the difference between the two main types of inverters and why this distinction matters for consumers.
Technical Differences: Break down the waveforms, technical functioning, and electrical properties of pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters.
When to Choose Pure Sine Wave: Describe situations where pure sine wave inverters are necessary (sensitive electronics like laptops, medical equipment).
When to Choose Modified Sine Wave: Explain where modified sine wave inverters work best (powering basic appliances, lights, fans).
Cost Comparison: Discuss price differences and the cost-effectiveness of each type for different needs.
Conclusion: Summarize which type is better suited for various applications.
Battery Maintenance 101: How to Extend the Life of Your Inverter Batteryv
Introduction: Start by highlighting the importance of maintaining your inverter’s battery to ensure long-lasting and reliable backup power.
Regular Charging Practices: Explain the importance of keeping the battery charged to avoid deep discharge, which can reduce battery lifespan.
Cleaning Terminals: Describe the process of cleaning the battery terminals to prevent corrosion, which affects performance.
Safe Installation: Discuss proper placement and installation, including keeping batteries away from excessive heat or moisture.
Proper Ventilation: Educate users about the need for adequate ventilation around the inverter and battery to prevent overheating.
Monitoring Battery Health: Recommend tools and methods for regularly checking battery health, such as using a multimeter.
Conclusion: Summarize best practices for making sure batteries last as long as possible.
The Benefits of Lithium-ion Batteries for Solar Inverter Systems
Introduction: Lithium-ion technology is revolutionizing energy storage for solar systems. Begin by emphasizing its growing popularity in the market.
Higher Efficiency: Explain how lithium-ion batteries charge faster and offer more efficient energy output compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Longer Lifespan: Highlight the longevity of lithium-ion batteries, which can last twice as long as conventional batteries, making them a better long-term investment.
Maintenance-Free: Mention that lithium-ion batteries require virtually no maintenance compared to the upkeep needed for lead-acid batteries.
Better Space Utilization: Talk about how lithium-ion batteries are more compact and offer better space efficiency, making them ideal for homes with limited space.
Environmentally Friendly: Highlight the eco-friendly aspects of lithium-ion technology, as they are more energy-efficient and produce fewer emissions.
Conclusion: Sum up the advantages and suggest why lithium-ion batteries may be the ideal choice for future solar inverter systems.
Top 5 Signs Your Inverter Battery Needs Replacement
Introduction: Let readers know that just like any other battery, inverter batteries have a finite lifespan. Explain why recognizing the signs of battery failure is crucial for maintaining an uninterrupted power supply.
Reduced Backup Time: Explain that a reduced backup time, despite regular charging, is the first and most noticeable sign of a failing battery.
Battery Swelling or Leaking: Describe how physical changes like bulging or leaking fluid are clear indicators of internal damage and should not be ignored.
Frequent Low Battery Warnings: Discuss how constant low battery alarms despite a full charge could mean the battery cells are dying.
Slow Charging: If the battery takes significantly longer to charge, this can indicate decreased capacity and efficiency.
Strange Noises or Smells: Address the importance of strange sounds or burning smells, which could mean internal battery faults.
Conclusion: Provide tips for choosing a replacement battery and when it’s time to upgrade to a newer, more efficient model.
How to Calculate Your Power Backup Needs for Homes and Offices
Introduction: Many users struggle to determine how much power they need for backup during an outage. This guide walks readers through the process of calculating their energy needs.
Understanding Load Requirements: Explain how to list essential devices that need power during an outage (lights, fans, routers, etc.) and calculate their wattage.
Determining Battery Capacity: Guide readers through the formula to calculate how much battery capacity is needed based on usage hours and power requirements.
Choosing the Right Inverter Size: Offer advice on picking an inverter with sufficient wattage to handle the calculated load, considering future expansions
.Considering Voltage and Efficiency Losses: Mention the importance of accounting for losses due to inverter inefficiency and voltage fluctuations.
Conclusion: End with a calculator tool or chart to simplify the process for users.
Inverter vs Generator: Which Backup Power Solution is Best?
Introduction: Help readers decide between two popular backup options—an inverter system or a generator.
- Cost Consideration: Compare the initial investment and ongoing fuel or battery costs for both inverters and generators.
- Noise and Environmental Impact: Explain that inverters are silent and eco-friendly, while generators produce noise and emissions.
- Maintenance Requirements: Discuss the regular maintenance needed for generators, such as oil changes and fuel storage, vs the minimal maintenance required for inverters.
- Power Output and Availability: Talk about how generators are better suited for prolonged outages with heavy load requirements, while inverters are ideal for shorter outages with moderate power needs.
- Ease of Use: Mention the convenience of automatic inverters vs the manual operation often required for generators.
Conclusion: Offer guidance on which solution is best based on different user needs, such as home vs business use.
Myths and Facts About Inverter Batteries
Introduction: Many consumers fall prey to common myths regarding inverter batteries, leading to poor decisions. This blog can help debunk these myths with facts.
- Myth 1: More Backup Time Equals Better Battery: Explain that battery quality and capacity are not always proportional to backup time. It depends on energy efficiency and usage.
- Myth 2: Only Expensive Batteries are Good: Clarify that several budget-friendly battery brands offer excellent performance.
- Myth 3: Batteries Don’t Require Maintenance: Bust the myth that batteries don’t need care, highlighting maintenance tips like cleaning and charging.
- Myth 4: All Inverter Batteries are the Same: Talk about how different technologies (lead-acid, tubular, lithium-ion) impact performance.
Conclusion: Clear up confusion and direct users toward informed decision-making when purchasing inverter batteries.
The Future of Inverters: Smart Inverters for Home Automation
Introduction: Technology is rapidly evolving, and inverters are no exception. Smart inverters are changing the way we interact with energy management in our homes.
- What is a Smart Inverter?: Explain the technology behind smart inverters and how they differ from traditional inverters.
- Integration with Smart Homes: Discuss how smart inverters can be integrated with home automation systems to remotely monitor and control power usage.
- Energy Management Features: Highlight smart features like energy consumption tracking, automatic switching between grid and battery power, and app-based controls.
- Improved Efficiency: Explain how these devices can optimize energy usage and reduce overall electricity costs by managing peak loads.
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness: Talk about how smart inverters play a role in building sustainable, energy-efficient homes.
Conclusion: Position smart inverters as the future of home energy management and explain why upgrading to one is a good long-term investment
Solar Inverters: How They Work and Why You Need One for Your Solar Setup
Conclusion: Summarize the importance of inverters in solar systems and encourage investment in high-quality, durable solar inverters for efficient power usage.
Introduction: For homes and companies switching to solar, understanding the role of inverters is crucial. This blog would explain how solar inverters work.
Topics to Cover:
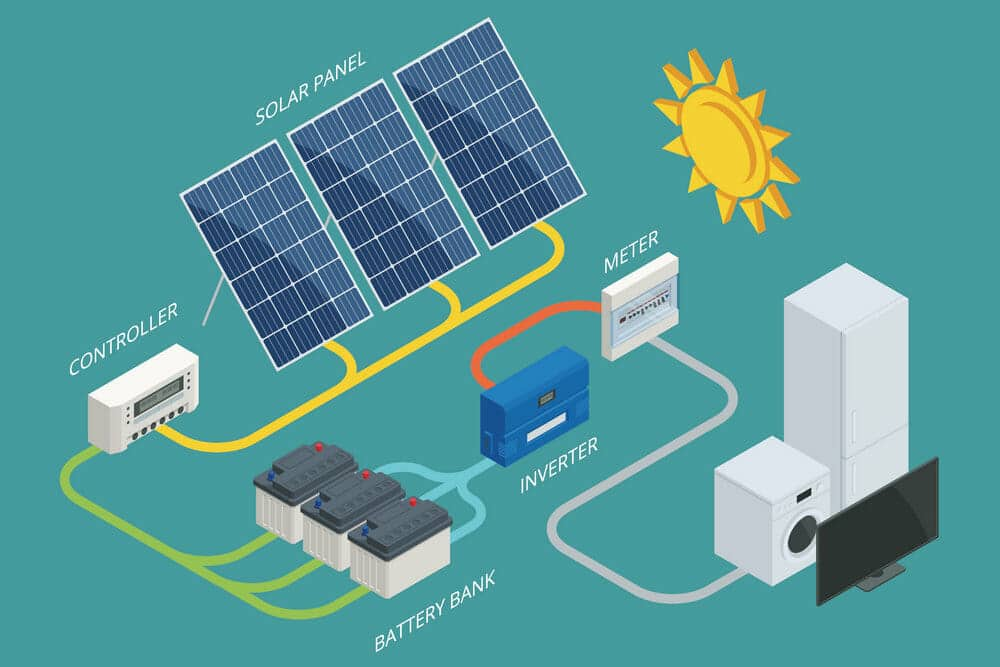
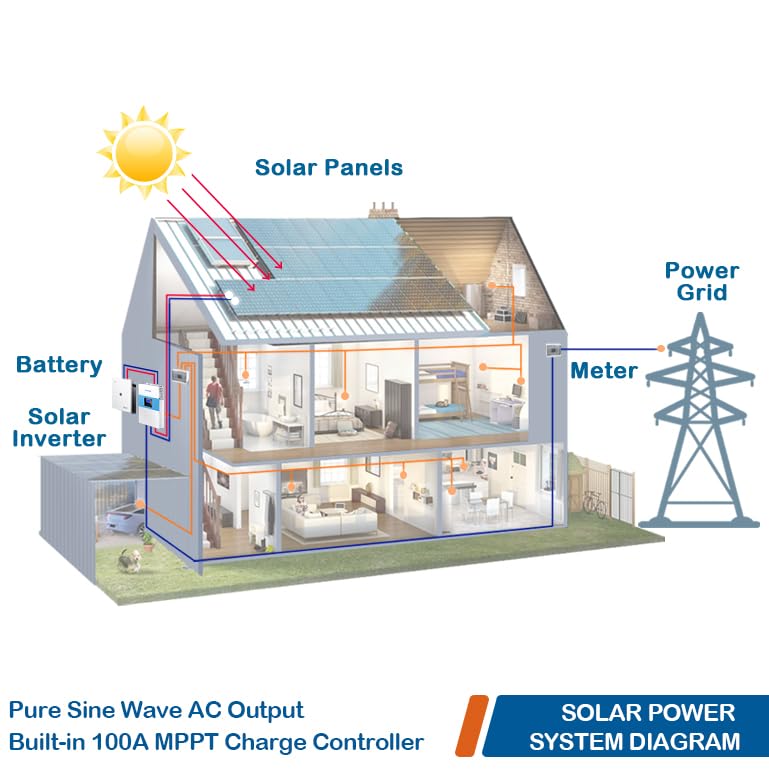
What is a Solar Inverter?: Begin by explaining the basic function of a solar inverter in converting DC power generated by solar panels into usable AC power.
Types of Solar Inverters: Discuss the different types, such as grid-tie, off-grid, and hybrid inverters, and where each is applicable.
Why Solar Inverters are Essential: Explain why a solar system cannot work efficiently without a proper inverter.
Battery Storage and Inverters: Explore how hybrid inverters manage both solar panels and battery storage systems for optimal energy usage.
Choosing the Right Solar Inverter: Provide tips on choosing the best solar inverter based on capacity, efficiency, and compatibility with solar systems.